Every year, over two million people in the U.S. enter correctional facilities, with a significant portion suffering from untreated mental health issues. This startling statistic highlights the urgent need for improved mental health care within prison systems. It begs the question: how can we better support these individuals?
Historically, mental health has been undervalued in prisons, but recent efforts have shown promising results. Providing access to therapy, medication, and support groups can significantly reduce the incidence of recidivism. Studies indicate that inmates participating in mental health programs are 25% less likely to re-offend, making it a vital component of prison reform.
- Increase funding for mental health services to improve quality and availability.
- Provide specialized training for prison staff on mental health awareness.
- Implement peer support programs to foster a supportive community among inmates.
- Conduct regular mental health screenings for early identification and intervention.
- Facilitate family involvement in mental health care to offer emotional support.
- Partner with local mental health organizations to enhance service delivery.
The Prevalence of Mental Health Issues in Prisons
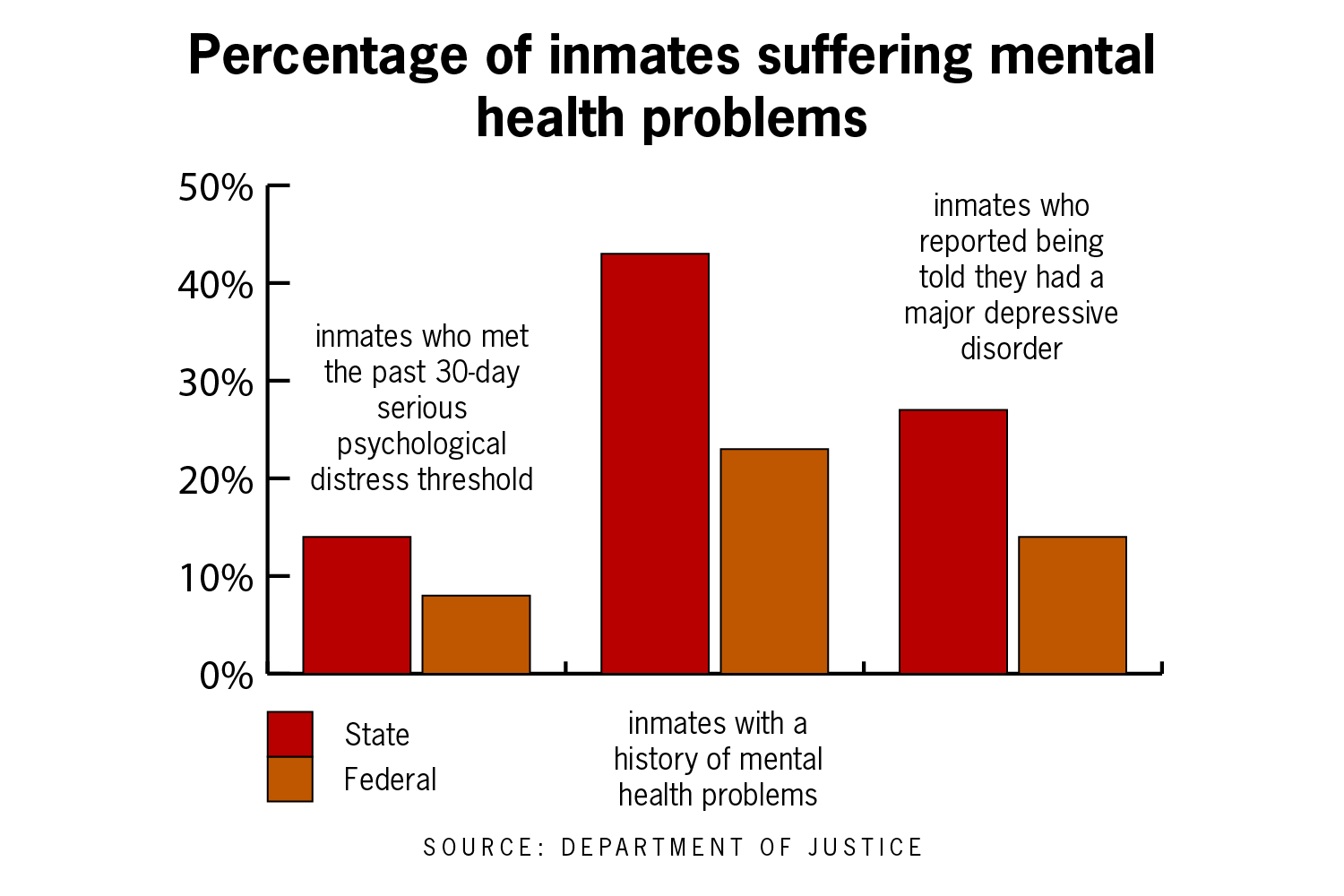
In the U.S., over 50% of inmates report having some form of mental health issue. This number is significantly higher than the general population. It highlights a critical need for better mental health care.
Many inmates enter prison already affected by mental health disorders. The stressful environment of a prison can worsen these conditions. This makes it challenging for them to cope and function.
Common mental health issues include depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These conditions can lead to behavioral problems if left untreated. Unfortunately, resources are often limited.
Without proper care, inmates with mental health issues are more likely to re-offend. Improving mental health services could help reduce recidivism. This would benefit both the individuals and society as a whole.
The Impact of Prison Environment on Mental Health
The prison environment can significantly affect inmates’ mental health. Harsh conditions and isolation often worsen existing issues. It’s essential to understand these impacts to improve care.
Effects of Overcrowding
Overcrowding is a common problem in many prisons. This can lead to increased anxiety and stress among inmates. When space is tight, conflicts are more likely to occur.
With too many people in one place, privacy is almost non-existent. This constant invasion can erode mental well-being. Inmates often feel like they can’t escape.
Overcrowded prisons also strain resources. There are fewer opportunities for mental health support. This creates a cycle of worsening conditions.
Solitary Confinement
Solitary confinement is used as a punishment in many prisons. However, it can have severe mental health repercussions. Inmates in solitary often experience heightened feelings of despair.
Extended isolation can lead to hallucinations and paranoia. The lack of human contact is extremely damaging. Even short-term solitary can be harmful.
Studies show that solitary confinement often worsens pre-existing mental health issues. It’s a severe measure with lingering effects. Many experts argue for its limited use.
Access to Mental Health Services
The availability of mental health services in prisons is limited. Many inmates don’t receive the care they need. This neglect can exacerbate problems.
Without proper support, inmates struggle to manage their mental health. This makes rehabilitation more difficult. Adequate services could help prevent future issues.
Providing better mental health care requires both funding and trained professionals. Improving access can lead to positive outcomes. It’s a necessary step for reform.
Existing Mental Health Services in Prisons: An Overview
Many prisons offer basic mental health services to inmates. These usually include counseling and access to medication. However, the quality and availability can vary widely.
Counseling is often provided by mental health professionals or trained staff. Group therapy sessions are another common approach. These services aim to help inmates manage stress and anxiety.
Medication is prescribed for conditions like depression and anxiety. In some prisons, inmates have regular check-ins with psychiatrists. But there can be challenges in ensuring consistent treatment.
Despite these services, demand often exceeds supply. Many inmates still struggle to get the care they need. Improving these services is crucial for effective rehabilitation and reducing recidivism.
Effective Methods to Enhance Mental Health Care in Prisons
One effective way to improve mental health care in prisons is to increase funding for mental health services. More resources mean better facilities and more qualified staff. This can lead to higher quality care.
Training prison staff in mental health awareness is also crucial. Staff can learn to recognize signs of mental health issues and respond appropriately. Proper training makes a big difference in inmates’ well-being.
Introducing peer support programs can be very beneficial. Inmates who have received mental health training can support each other. This creates a sense of community and reduces feelings of isolation.
Regular mental health screenings help identify issues early. Early intervention can prevent conditions from worsening. Periodic check-ups ensure inmates receive the care they need.
Allowing family involvement in mental health care can also help. Family members often provide valuable emotional support. This connection can aid in the inmate’s mental health recovery.
Another method includes partnering with local mental health organizations. External experts can bring specialized services to the prison. These partnerships enhance the overall quality of mental health care.
The Role of Aftercare Post-Release in Preventing Recidivism
Aftercare services are critical for inmates re-entering society. These services offer continued mental health support, helping former inmates adjust. Without aftercare, many struggle to cope, increasing the risk of re-offending.
Providing counseling and therapy sessions post-release is essential. This support helps address ongoing mental health issues. Regular check-ins with mental health professionals can make a huge difference.
Connecting released inmates with community resources is also beneficial. Support groups and mentor programs offer guidance. These connections help former inmates feel less alone.
- Job training programs
- Housing assistance
- Substance abuse programs
Programs that assist with basic needs, like finding housing and employment, are crucial. Stability in these areas reduces stress. This stability contributes positively to mental health and lowers recidivism rates.
Collaboration between prisons and local mental health organizations can enhance aftercare. These partnerships bring specialized services to those in need. Strengthening these networks offers a better safety net for former inmates.
Key Takeaways
- Funding for mental health services helps improve care quality.
- Training staff on mental health awareness is crucial.
- Peer support programs offer valuable community for inmates.
- Regular screenings help identify issues early.
- Partnering with local organizations enhances service delivery.

Frequently Asked Questions
Improving mental health care in prisons is vital for effective rehabilitation. Here are some common questions and their answers to help you understand better.
1. Why is mental health care important in prisons?
Mental health care in prisons helps inmates manage their conditions, reducing stress and preventing issues from worsening. Without proper treatment, many prisoners struggle, leading to increased conflicts and difficulty reintegrating into society post-release.
Providing adequate mental health services can lower the rates of re-offending by addressing underlying issues. This support plays a crucial role in preparing inmates for life outside prison, making communities safer.
2. What types of mental health disorders are common among inmates?
Common mental health issues among inmates include depression, anxiety, PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder), and substance abuse disorders. These conditions are often exacerbated by the stressful environment of prison life.
Many inmates enter the system with pre-existing conditions that may not have been treated adequately. Addressing these disorders through therapy and medication can significantly improve their well-being and behavior while incarcerated.
3. How do peer support programs benefit inmates’ mental health?
Peer support programs help create a supportive community among inmates, offering emotional support and understanding from those who have faced similar struggles. These programs encourage positive relationships and personal growth.
Inmates trained as peer counselors can provide valuable guidance, fostering trust within the prison community. Such initiatives can reduce feelings of isolation and boost overall morale.
4. How does family involvement aid in an inmate’s mental health recovery?
Family involvement provides emotional support that can be crucial for an inmate’s recovery process. Regular contact with loved ones helps maintain connections to the outside world and offers hope for a better future.
This support network can motivate inmates to participate in rehabilitation programs more actively. It also aids in smoother transitions back into society upon release.
5. What challenges exist in providing adequate mental health care in prisons?
The main challenges include limited resources, insufficient funding, and a shortage of qualified mental health professionals within the prison system. These constraints can hinder comprehensive care provision.
Overcrowded facilities make it difficult to deliver personalized treatment plans, while stigma surrounding mental illness may prevent inmates from seeking help voluntarily. Tackling these issues requires systemic changes and increased investment.

Conclusion
Improving mental health care in prisons is essential for the well-being of inmates and society. By providing comprehensive support, we can help inmates manage their conditions and reduce re-offending rates. This requires a commitment to funding, training, and innovative programs.
Enhanced mental health services benefit everyone involved. Inmates gain the tools they need for rehabilitation, and communities become safer. Investing in these improvements is a step towards a more just and effective prison system.
